Pigment producing pathogenic bacteria:
Pseudomonas species
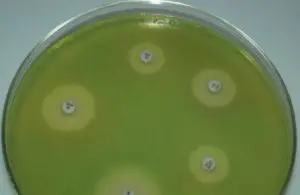
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a leading bacterial pathogen in hospital settings and for immunocompromised patients (those with underlying conditions such as neutropenia, burns or cystic fibrosis). P. aeruginosa ( aeruginosa, which derives from a Latin word denoting the color of copper rust) produces a green fluorescent pigment (fluorescein/pyoverdin) and a blue pigment (pyocyanin). These pigments impart greenish hue to the sputum of cystic fibrosis patients with chronic lung infection, gives colonies and infected wound dressings a greenish-blue coloration.
P. aeruginosa is usually recognized by the pigments it produces and the distinctive smell of cultures. . When the culture is left at room temperature, pigment colour becomes more intense. A minority of strains are non-pigment producing.
Other species of Pseudomonas (such as P.fluorescens and P. putida) also produce pigments.
Other species of Pseudomonas (such as P.fluorescens and P. putida) also produce pigments.
Serratia
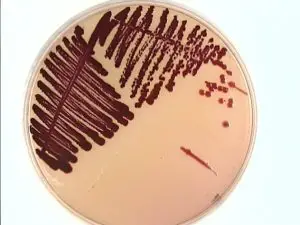
Serratia marcescens (mneomonic: Mars is red) is notable for its production of a bright red pigment called “prodigiosin”. Some strains produce a red pigment in nutrient agar at room temperature
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus (aureus = “golden”, Latin) produces multiple carotenoid pigments, one being golden yellow pigment (Staphyloxanthin). When cultured on sheep blood agar, S. aureus can be differentiated from other beta-hemolytic cocci by elaboration of golden pigment. Pigment is less pronounced in young colonies.
Violacein from Chromobacterium violaceum
Chromobacterium violaceum, an agent of localized skin infection or localized lymphadenitis which occasionally causes fatal septicemia elaborates a blue-violet pigment, violacein.
Group B Streptococcus
Group B Streptococcus (GBS), the leading etiologic cause of severe neonatal bacterial infection, expresses an orange-red pigment, called granadaene. This Orange pigment is produced by Streptococcus agalactiae when cultured on serum starch agar anaerobically.
Iron porphyrin of Porphyromonas gingivalis
Porphyromonas gingivalis is a gram negative anaerobic bacilli, which is implicated in the pathogenesis of certain forms of periodontal disease. Arginine- and lysine-specific gingipain proteases of P. gingivalis degrade hemoglobin to release iron (III) protoporphyrin IX , which is dimerized to form the micro-oxo bis-haem-containing black pigment of the organism.
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria
The genus Mycobacterium includes many bacteria that produce pigments. . The Runyon classification systemgroups mycobacteria based on growth rate and pigment production in the presence of light or dark. M. tuberculosis is a nonchromogen, i.e. it does not produce pigment in light or darkness
Fungal pathogens which produce pigments
Aspergillus fumigatus is a filamentous fungus that elaborates a melanin-like substance during its conidial stage of growth.
Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated yeast-like fungus that produces a brown or black melanin pigment by conversion of diphenols or homogentisic acid this coloration can be used for rapid identification of colonies on cornmeal agar, a medium commonly used in yeast isolation
Penicillum marneffei is an opportunistic pathogen causing systemic penicilliosis in AIDS patients. It produces characteristic red pigment in Sabouraud dextrose agar.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment