A. Functions
1. Produce male germ cells (spermatozoa)
2. Produce male hormone (testosterone)
3. Produce inhibin
and estrogen, and other proteins
B. Structure
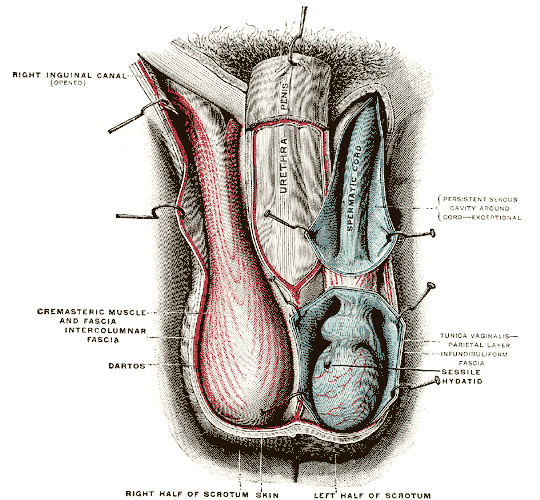
1. Tunica vaginalis
a. Thin membrane
b. Provides support
c. From peritoneum
2. Tunica albuginea
a. Connective tissue
b. Provides structure
3. Mediastinum
a. Connective tissue
- Provides internal support4. Seminiferous tubulespart of the testicular parenchymaa. Site of sperm productionb. Consists of 2 cell types- Germ cells (eventual sperm cells)- Sertoli or nurse cells which produces variety of substances including androgen binding hormone, sulfated glycoprotein, transferin, and inhibin- Surround developing germ cells- Providing structural and metabolic support to the developing spermatogenic cells3. Blood-testis Barriersa. Cells surrounding the seminiferous tubulesb. Prevent autoimmune reaction from destroying the developing germ cells5. Interstitial or Leydig cellsa. Located between seminiferous tubulesb. Produce androgens (testosterone)6. Rete testisa. Collect sperm from seminiferous tubules7. Vasa efferentia (efferent ductules)a. Collect sperm from rete testisb. Carry sperm out of testis proper


0 Comments:
Post a Comment