Mean, Variance, and Standard Deviation
Consider the following.The definitions for population mean and variance used with an ungrouped frequency distribution were:
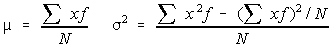
Some of you might be confused by only dividing by N. Recall that this is the population variance, the sample variance, which was the unbiased estimator for the population variance was when it was divided by n-1.
Using algebra, this is equivalent to:
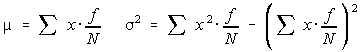
Recall that a probability is a long term relative frequency. So every f/N can be replaced by p(x). This simplifies to be:
What's even better, is that the last portion of the variance is the mean squared. So, the two formulas that we will be using are:
Here's the example we were working on earlier.
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | sum |
| p(x) | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 1/6 | 6/6 = 1 |
| x p(x) | 1/6 | 2/6 | 3/6 | 4/6 | 5/6 | 6/6 | 21/6 = 3.5 |
| x^2 p(x) | 1/6 | 4/6 | 9/6 | 16/6 | 25/6 | 36/6 | 91/6 = 15.1667 |
The variance is 91/6 - (7/2)^2 = 35/12 = 2.916666...
The standard deviation is the square root of the variance = 1.7078
Do not use rounded off values in the intermediate calculations. Only round off the final answer.
You can learn how to find the mean and variance of a probability distribution using lists with the TI-82 or using the program called pdist.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment