This is where the Scheffe' and Tukey tests come into play. They will help us analyze pairs of means to see if there is a difference -- much like the difference of two means covered earlier.
Hypotheses
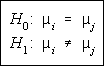 Both tests are set up to test if pairs of means are different. The formulas refer
to mean i and mean j. The values of i and j vary, and the total number of tests
will be equal to a combination of k objects, 2 at a time C(k,2), where k is the
number of samples.
Both tests are set up to test if pairs of means are different. The formulas refer
to mean i and mean j. The values of i and j vary, and the total number of tests
will be equal to a combination of k objects, 2 at a time C(k,2), where k is the
number of samples.Tukey Test
The Tukey test is only usable when the sample sizes are the same.The Critical Value is looked up in a table. It is Table N in the Bluman text. There are actually several different tables, one for each level of significance. The number of samples, k, is used as a index along the top, and the degrees of freedom for the within group variance, v = N-k, are used as an index along the left side.
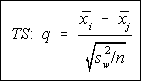 The test statistic is found by dividing the difference between the means
by the square root of the ratio of the within group variation and the
sample size.
The test statistic is found by dividing the difference between the means
by the square root of the ratio of the within group variation and the
sample size.
Reject the null hypothesis if the absolute value of the test statistic is greater than the critical value (just like the linear correlation coefficient critical values).

0 Comments:
Post a Comment