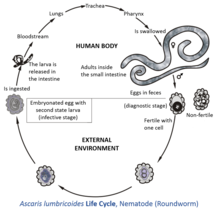
Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms"

Morphology of Ascaris:
- Adult: cylindrical shape, creamy white or pinkish in color
- Male: average 15–30 cm and is more slender than female
- Female: average 20–35 cm in length.
Pathogenesis :
Main pathologic events occur during pre patent stage.
-
In heavy infection, the
migrating larva may cause severe damage & mechanical destruction
-
Hypersensitivity and allergic
reaction.
-
The fibrotic liver after
inflammation heals, gives rise to so called “Milk spot” or “white spot” lesions
& made whole liver unfit for human
consumption.
-
Hemorrhage may occur in liver
& in most cases lung.
-
Lung hemorrhages can be
followed by desquamation of alveolar epitheliums, edema & infiltration of
the eosinophils & other cells in pulmonary parenchyma.
-
Extensive lung lesions give
rise to clinical signs of severe respiratory embarrassment (thumps) where
breathing is rapid, shallow & marked by forcible expiratory efforts &
cocarisughing & pigs may die.
-
Death from severe lung damage
in 15 days after infection.
-
Numerous adult parasites may
form a bundle and create intestinal obstruction.
-
Ascarids may wander and cause
vomition, biliary obstruction in bile duct thus biliary stasis and can produce
peritonitis.
-
Adlt may create diarrhoea by
interference with proper nutrition and normal growth.
-
Depends on severity of
infection.
-
Severe respiratory distress in
growing pig.
-
Malnutrition and lesions of
interstitial pneumonia.
-
Hepatic fibrosis &
diarrhoea in some case.
-
Pneumonia in heavily infected
newborn pigs especially a cough & exudates into the lungs.

Diagnosis
-
Clinical & necropsy
findings.
-
Demonstration of larva in sputum in early stage.
-
Presence of Ascaris egg in the
faeces. (Sometimes due to coprophagia pigs may shed egg in feces without having
adult in their intestine, thus false
positive result can occur)
Treatment
-
Migrating larva is not affected
by anthelminties.
For adult
- Piperazives 100-400
ng/kg with food.
- Dichlorlos orally @ 10
mg/kg.
-
Regular anthelmintic
medication.
-
Good sanitation at furrowing.
-
Limited access of baby pig to
contamination.
Source
- healthline.com
- Wikipedia.org
- Cvasu Parasitology Notes
- Medical Parasitology



0 Comments:
Post a Comment