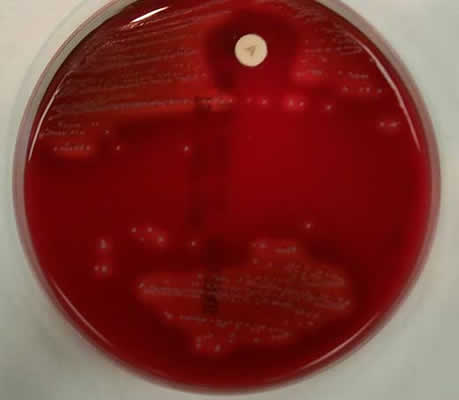
This is a differential test used to distinguish between organisms sensitive
to the antibiotic bacitracin and those not. Bacitracin is a peptide
antibiotic produced by Bacillus subtilis. It inhibits cell wall
synthesis and disrupts the cell membrane. This test is commonly used
to distinguish between the b-hemolytic streptococci:
Streptococcus agalactiae (bacitracin resistant) and Streptococcus
pyogenes (bacitracin sensitive). The plate below was streaked with
Streptococcus pyogenes; notice the large zone of inhibition
surrounding the disk.
 Taxos A (bacitracin sensitivity
testing)
Taxos A (bacitracin sensitivity
testing)



0 Comments:
Post a Comment