Catalase Test
This test is used to identify organisms that produce the enzyme, catalase.
This enzyme detoxifies hydrogen peroxide by breaking it down into water
and oxygen gas.
The bubbles resulting from production of oxygen gas clearly
indicate a catalase positive result. The sample on the right below is
catalase positive. The Staphylococcus spp. and the Micrococcus
spp. are catalase positive. The Streptococcus and
Enterococcus spp. are catalase negative.
Oxidase Test
This test is used to identify microorganisms containing the enzyme cytochrome
oxidase (important in the electron transport chain). It is commonly
used to distinguish between oxidase negative Enterobacteriaceae
and oxidase positive Pseudomadaceae.
Cytochrome oxidase transfers electrons from the electron transport chain
to oxygen (the final electron acceptor) and reduces it to water. In
the oxidase test, artificial electron donors and acceptors are provided.
When the electron donor is oxidized by cytochrome oxidase it turns a
dark purple. This is considered a positive result. In the picture below
the organism on the right (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) is oxidase
positive.
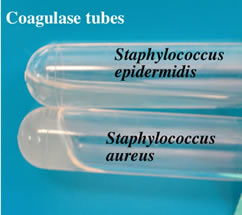
Coagulase test
Coagulase is an enzyme that clots blood plasma. This test is performed on Gram-positive, catalase positive
species to identify the coagulase positive Staphylococcus aureus. Coagulase is a virulence factor of S. aureus. The formation
of clot around an infection caused by this bacteria likely protects
it from phagocytosis. This test differentiates Staphylococcus aureus from other coagulase negative Staphylococcus species.







0 Comments:
Post a Comment