The nail complex is the structural and functional unit of the nail. The nail consists of the plate; bed; matrix; proximal, lateral, and distal grooves; proximal and lateral folds; and hypochondriac (see the image below) Aside from being aesthetically appealing, the healthy nail unit has the important function of protecting the distal phalanges, fingertips, and surrounding soft tissues from external injury, as well as enhancing precise delicate movements of the distal digits through the mechanistic action of counter-pressure exerted over the valor skin and pulp.
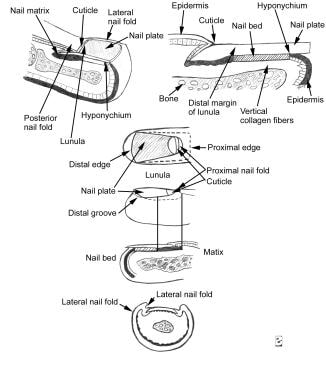 Longitudinal section of a digit showing the dorsal nail apparatus (top). Component part of the nail apparatus (bottom).
Longitudinal section of a digit showing the dorsal nail apparatus (top). Component part of the nail apparatus (bottom).
See 15 Fingernail Abnormalities: Nail the Diagnosis, a Critical Images slideshow, to help identify conditions associated with various nail abnormalities.
Performing successful nail surgery requires a comprehensive understanding of nail anatomy and physiology.[6, 7] An understanding of both the vascular and neural pathways supplying the nail complex and the functions and relationship of each component of the nail unit is also essential. Thus, the nail surgeon should be equipped with knowledge of nail pathology, surgical techniques and instrumentation, anesthesia, preoperative evaluation, management of complications, and wound care and healing after surgery. This knowledge ensures minimal patient discomfort, maximal patient satisfaction, and optimal surgical success. With these goals in mind, this article reviews the nail anatomy and focuses on common nail pathologies with the corresponding surgical techniques used for their diagnosis and treatment.


0 Comments:
Post a Comment